Data Update 3: Inflation and its Ripple Effects!
Inflation numbers have been coming in high now, for more than a year, but for much of the early part of 2021, bankers, investors and politicians seemed to be either in denial or casually dismissive of its potential for damage. Initially, the high inflation numbers were attributed to the speed with the economy was recovering from COVID, and once that excuse fell flat, it was the supply chain that was help responsible. By the end of 2021, it was clear that this bout of inflation was not as transient a phenomenon as some had made it out to be, and the big question leading in 2022, for investors and markets, is how inflation will play out during the year, and beyond, and the consequences for stocks, bonds and currencies.
Inflation: Measurement and Determinants
As the inflation debate was heating up in the middle of last year, I wrote a comprehensive post on how inflation is measured, what causes it and how it affects returns on different asset classes. Rather than repeat much of that post, let me summarize my key points.
-
Measuring inflation is not as simple as it looks, and measures of inflation can vary depending on the basket of good/services used, the perspective adopted (consumer, producer, GDP deflator) and the sampling used to collect prices. That said, the three primary inflation indices in the US, the CPI, the PPI and the GDP deflator all told the same story in 2021:
Download historical inflation numbers The inflation rate during the course of the year reached levels not seen in close to 40 years, with every price index registering a surge. -
While news stories focus on reported (and past0 inflation, it is expected inflation that should drive investment, and measures of these expectations can come from surveys of consumers (University of Michigan) or from the market, as the difference between the treasury bond rate and the inflation-protected treasury bond, of equivalent maturity:
Download data Using the ten-year bond, it is clear that while inflation expectations have inched up in the bond market, but that rise is far more muted than in the actual inflation indices, and consumer expectations of inflation now significantly exceed the bond-market imputed estimate for expected inflation. -
While the implied inflation in bond rates is low, investors seem to be anticipating higher inflation. Using a measure that the Federal Reserve has developed, I report the percent of investors expecting inflation to be greater than 2.5%, representing one end of the inflation expectation spectrum, and those expecting deflation, representing the other, in the graph below:
Download data As you can see the 93.96% of investors were expecting inflation to be greater than 2.5%, by the end of December 2021, up from 6.74% in December 2020, suggesting a sea change in the market. Conversely, the percent of investors expecting deflation has dropped to a vanishing low number, suggesting that Cathie Wood has little company, in her contention that deflation is the real danger to markets and economies.
Interest Rates and Inflation
Inflation and interest rates are intertwined, and when their paths deviate, as they sometimes do, there is always a reckoning. While we have increasingly given central banks primacy in discussions of interest rates, it remains my view that markets set rates, and while central banks can nudge market expectations, they cannot alter them. Put simply, no central bank, no matter how powerful, can force market interest rates down, if inflation expectations stay low, or up, if investor are anticipating high inflation.
US Treasuries: A Mostly Uneventful Year
After a turbulent year in 2020, when COVID shut the global economy down, and interest rates plunged and stayed down for the rest of the year, 2021 was a more settled year, with long term rates rising gradually over the course of the year, but short terms rates staying put:
 |
| Treasury Rates Data |
While treasury bills continued to yield rates close to zero, rates increased for longer term treasuries, with 2-10 years rates rising much more than rates on the longest term treasuries (20-year to 30-year). For those who track the slope of the yield curve, and I am not one of those who believes that it has much predictive power, it was a confusing year. The treasury curve became steeper, but only at the shortest end of the spectrum, with the slope rising for the 2-year, relative to the 3-month, but not at all, when comparing the 10-year to the 2-year rate. Beyond the 10-year maturity, the slope of the yield curve actually flattened out, with the difference between the 30-year rate and the 10-year rate declining by 0.34%.
Corporate Bonds: No Shortage of Risk Capital
In my last post, I chronicled the movement in the equity risk premium, i.e. the price of risk in the equity market, during 2021, but the bond market has its own, and more measurable, price of risk in the form of corporate default spreads. Using bond ratings classes to categorize companies, based upon credit risk, I looked at the movement of default spreads during 2021:
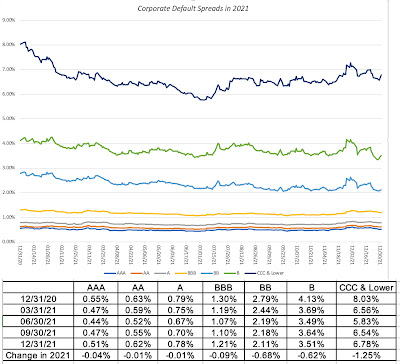 |
| Download data |
Corporate default spreads decrease across ratings classes, but the decline is much larger for lower rated bonds, with the default spread on high yield bonds registering a drop of 1.25%. Note that the decrease in default spreads, at least for the lower ratings, mirrors the drop in the implied equity risk premium during the course of 2021. Read together, it suggests that private risk capital continued to not just stay in the game, but increased its stake during the course of the year, extending a decade-long run.
Expected Inflation, Interest Rates and Bond Returns
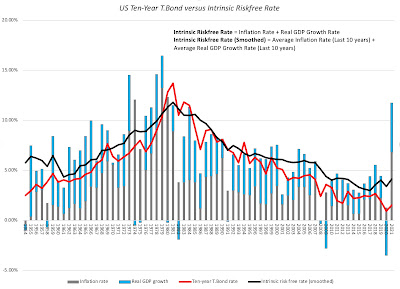
While day to day movements in interest rates are driven by multiple forces, including the latest smoke signals coming from central banks and investor sentiment, the longer term and drivers of interest rates are fundamental. In particular, if you start by breaking down a long term riskfree rate (like the 10-year treasury bond) into an expected inflation and an expected real interest rate components, you can also reconstruct an intrinsic risk free rate by assuming that the real growth in the economy is a stand-in for the real interest rate and that most investors form expectations of future inflation by looking at the inflation in the most recent year(s):
 |
| Download data |
In this picture, ythe actual ten-year treasury bond rate is superimposed against a rough measure of the intrinsic risk free rate (obtained by adding together the actual inflation rate and real growth rate each year) and a smoothed out version (where I used the average inflation rate and real growth rate over the previous ten years). Not only has the intrinsic risk free rate moved in sync with the ten-year bond rate for most of the last seven decades, but you can also see that the main reason why rates have been low for the last decade is not the Fed, with all of its quantitative easing machinations, but a combination of low growth and low inflation. Coming into 2022, though, the intrinsic risk free rate is clearly running ahed of the ten-year treasury bond rate, and if history is any guide, that gap will close either with a rise in the treasury bond rate or a decline in the risk free rate (coming from a recession or a rapid drop off in inflation).
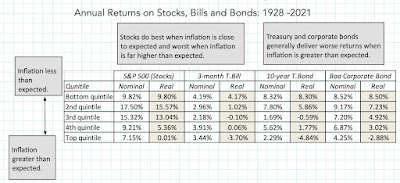
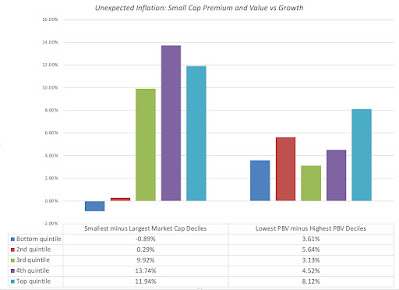
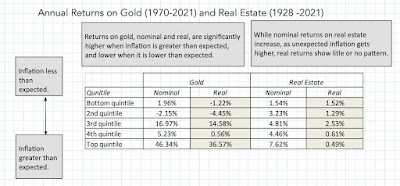
Unexpected Inflation and Asset Returns
Note that it is expected inflation that drives interest rates, and that the actual inflation rate can come in above or below expectations. In my post on inflation last year, I drew a contrast between expected and unexpected inflation, arguing that financial assets are affected differently by each component. If expected inflation is high, but it is predictable, investors and businesses have the opportunity to incorporate that inflation into their decision making, with investors demanding higher interest rates on bond and expected returns on stocks, and businesses raising prices on their products/services to cover expected inflation. Unexpected inflation is what catches us off guard, with unexpectedly high inflation leading to a reassessment of pricing (for all financial assets) and an uneven impact across businesses, leaving those with pricing power in a better position than those without that power.
To assess how inflation has affected asset returns over time, I broke down the actual inflation rates since 1954 into expected and unexpected components each year, using a brute force assumption that the average inflation rate over the last ten years is the expected inflation rate. (In the last two decades, we have had access to more sophisticated measures of expected inflation, including the difference between the nominal treasury bond and TIPs rates, but not in earlier years). In the graph below, I look at annual returns on stocks, treasury bonds and corporate bonds, with the unexpected inflation numbers also shown:
 |
| Download data |
Riskfree rates are highest in currencies, like the Zambian Kwacha or Turkish Lira, where inflation is highest, lower in low-inflation currencies and even negative in currencies, where deflation may be the long term prediction. I am using the default spreads based upon the local currency sovereign ratings for the countries in question, with the government bond rate being the risk free rate only for currencies where the issuing government in triple-A rated. If you dislike this assumption, or do not believe that the government bond rate is a market-set number in a particular market, there is a second approach, where you start with the risk free rate in US dollar or Euros, and adjust it for differential inflation, i.e., the difference in expected inflation between the US and the country in question:
Thus, if the US treasury bond rate is 1.5%, and expected inflation rates in the US and Indonesia are 1% and 4% respectively, the approximate riskfree rate in Indonesian Rupiah will be 4.5% (=1.5% + (4%-1%)) and the more precise riskfree rate in Rupiah will be 4.52% (=1.015*(1.04/1.01)-1). While the expected inflation rate in dollars may be an easy get, it is more difficult to get expected inflation rates in other currencies, but the IMF has estimates for the next five years at this link.
Thus, currencies with higher inflation can be expected currency devaluation over time, relative to currencies with lower inflation. As with interest rates, in the short term, there are forces, ranging from central banking intervention to momentum and speculation, that can cause rates to deviate from the inflation script, but in the long term, it is almost impossible to break the cycle.